Direct Selling or MLM? Understanding How They Work
Direct Selling or MLM? Understanding How They Work
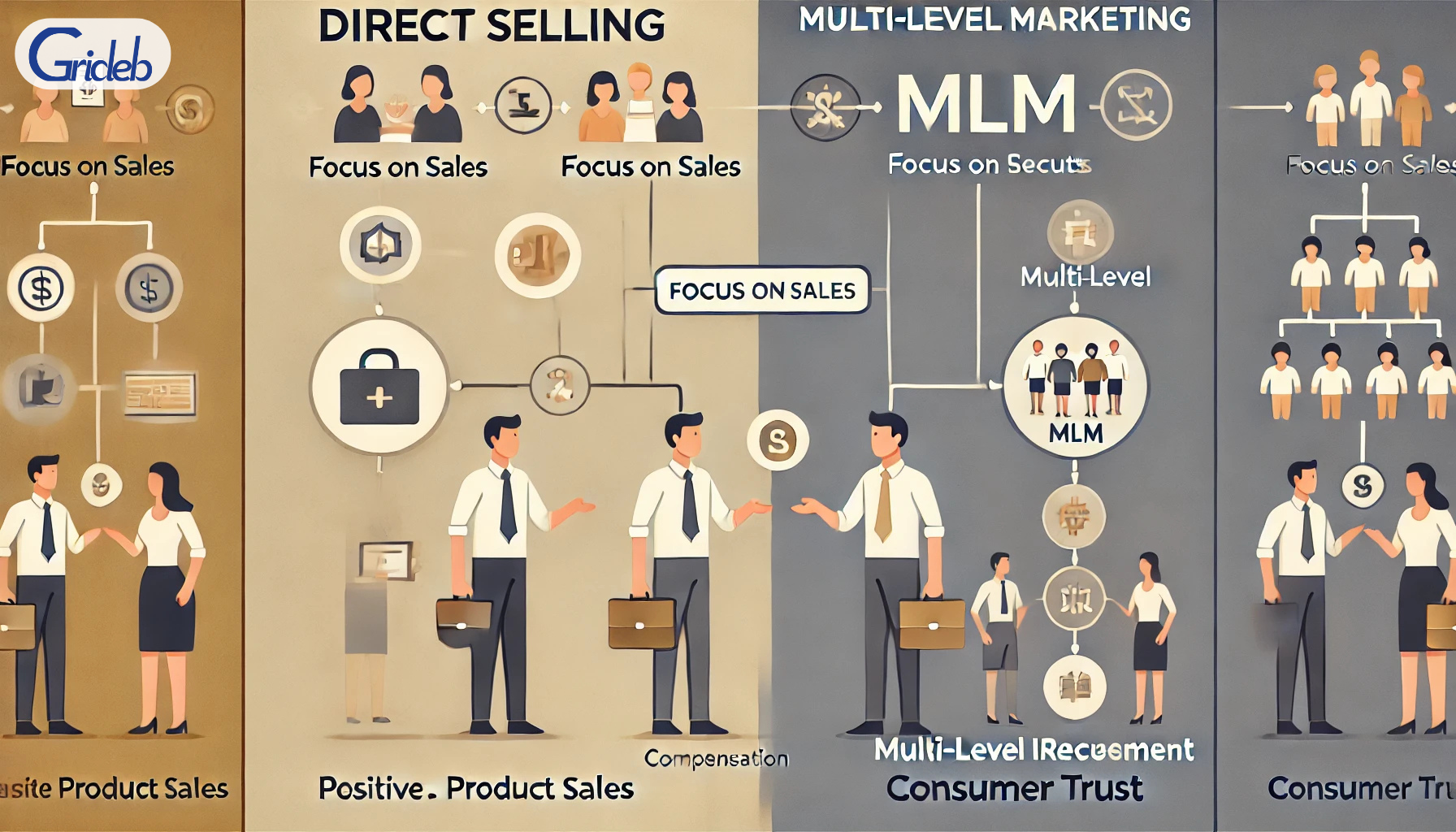
In today’s dynamic retail landscape, consumers encounter a variety of sales channels, including traditional stores, e-commerce, and innovative direct selling methods. Two commonly confused terms within this space are direct selling and multi-level marketing (MLM). While they may appear similar at first glance, these business models have distinct differences that significantly affect how they operate and how individuals can engage with them. Let’s delve into the definitions, compensation structures, recruitment focuses, product offerings, and more to shed light on what sets these two approaches apart.
Definitions
Direct Selling is a retail channel where products are sold directly to consumers outside of a fixed retail location. This often involves personal interactions, whether face-to-face at home parties or online through social media and e-commerce platforms. Representatives build relationships with customers and provide personalized service, which can lead to repeat business.
Multi-Level Marketing (MLM), on the other hand, is a specific type of direct selling where sales representatives earn income not only from their sales but also from the sales made by other representatives they recruit into the business. This model creates multiple income levels based on the recruitment of a sales team, potentially leading to significant earnings for those who build a large network.
Compensation Structure
The compensation structure is one of the most striking differences between direct selling and MLM. In direct selling, representatives typically earn a straightforward commission based solely on their sales. For instance, they might earn a flat percentage for every product sold, providing clear and predictable income.
In contrast, MLM compensation plans are more complex. Representatives can earn commissions on their sales as well as on the sales generated by their recruits. This structure can lead to exponential income potential, but it also means that income levels can vary widely among participants. According to the Direct Selling Association (DSA), around 30% of direct sellers in the U.S. are involved in MLMs, highlighting its popularity within the direct selling industry.
Recruitment Focus
The focus of each model is another differentiator. In direct selling, the primary emphasis is on selling products. While recruitment can play a role, it is not the central focus of the business model. Representatives concentrate on building customer relationships and promoting product sales.
Conversely, MLM places significant emphasis on recruitment. Many compensation plans are designed to reward representatives for bringing in new sales team members. The DSA reported that in 2022, approximately 82% of MLM sales came from distributors selling to their own networks. This recruitment-heavy focus can sometimes overshadow the product sales aspect, which can lead to a less favorable perception among consumers.
Product Range and Pricing
When it comes to product offerings, both models feature diverse product ranges but approach them differently. Direct selling typically involves a wide array of consumer goods, from cosmetics and skincare products to household items, often priced competitively compared to traditional retail outlets.
In contrast, MLM products are often marketed as premium or exclusive. Health and wellness products are particularly common in MLMs, with the market for such products valued at over $10 billion. This premium positioning can attract consumers, but it can also lead to skepticism regarding the true value of the products being sold.
Business Model Legitimacy
In terms of legitimacy, direct selling is generally regarded as a legitimate business model when it adheres to ethical guidelines. The DSA reports that direct selling contributes over $36 billion to the U.S. economy, underscoring its significance.
However, MLMs often face scrutiny regarding their business practices and the potential for pyramid scheme structures. Research indicates that only about 1% of MLM participants make a substantial income, raising concerns about the sustainability of the model and the experiences of the majority of participants.
Regulation and Oversight
Both models are subject to regulation and oversight. Direct selling is regulated by organizations like the DSA, which promotes ethical standards among its members. In contrast, MLMs face additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), which enforces anti-pyramid scheme laws to protect consumers.
Consumer Perception
The consumer perception of direct selling and MLM also varies widely. Direct selling is often viewed positively, as it fosters personal connections and community building. Consumers appreciate the personalized service and relationships they form with representatives.
MLM, however, can have a mixed reputation. Many consumers are wary of aggressive recruitment tactics and the high turnover rates among representatives. This skepticism can hinder trust in the products and the business model itself.
Market Growth
Despite their differences, both direct selling and MLM are experiencing growth. The direct selling industry saw a reported 6.4% increase in sales in 2021, demonstrating its resilience in a changing marketplace. Meanwhile, MLM remains a significant segment of this industry, with millions of individuals participating globally. In 2020, the global MLM market was valued at approximately $178 billion, indicating its considerable impact.
Conclusion
In summary, while direct selling and MLM share similarities as non-traditional sales channels, they fundamentally differ in their compensation structures, recruitment focuses, and consumer perceptions. Understanding these distinctions can empower individuals to make informed decisions about engaging with these sales models, whether as consumers or potential representatives. As the retail landscape continues to evolve, both models will likely adapt, but the core differences will remain relevant for anyone navigating this space.







